You are born in Fiji in 1910. Your parents were brought from India by the British to work in the sugarcane fields as indentured laborers. Now they are free of debt and own farmland. The public school is OK, but your parents want you to go to the best private school. The principal there says you must leave Hinduism and convert to his religion before you can enroll.
What do you think your parents would do?
What You Will Learn…
Main Ideas
1. Hinduism has spread outside of India several times.
2. Hinduism is the third largest religion in the world.
3. Hindus practice religion at home and in temples and through the many festivals.
The Big Idea
Building Background Hinduism is the only major religion from the distant past that is still vibrant today. It survived because of its tradition of home-centered worship, because of its rich teachings and many religious leaders, and because it is not merely tolerant of other religions but respects the validity of all spiritual paths.
Traditions and Holy Days
Hinduism is the oldest living religion in the world. There are today nearly a billion Hindus worldwide, 95 percent of whom live on the Indian subcontinent. Hinduism continues to thrive for many reasons. Its followers find answers to their deepest questions about the mysteries of life. With personal religious practices, pilgrimage to sacred shrines, temple- and home-centered worship, Hindus strive for God Realization. And through celebration of the yearly cycle of vibrant and colorful festivals, they experience great blessings and joy.
Basic Practices
There are five basic practices, pancha nitya karmas, often observed by Hindus. They are to: 1) worship daily, 2) follow dharma, 3) observe the sam-skaras (rites of passage), 4) celebrate the holy days and 5) go on pilgrimage to sacred places. Other practices include meditation, chanting of mantras, study of scripture, hatha yoga and other yoga techniques, and simple austerities, such as fasting. There are many samskaras, including a child’s name-giving ceremony, the first feeding of solid food, the beginning of formal education and marriage. It is a common practice for Hindu women to wear a bindi, a red dot on the forehead. A similar mark, called tilaka, is worn by men at the temple or on ceremonial occasions. This forehead mark symbolizes many things, especially spiritual vision.
Worship in the Home
Every Hindu home has a place of worship. It may be as simple as a shelf with pictures of God or an entire room dedicated to worship. Many families have a spiritual guide or guru whose picture is displayed in the shrine. There, the family may light a lamp, ring a bell and pray daily. The most devout hold a formal morning worship ritual. They offer flowers, incense, lights and food to God while chanting sacred verses. Individual members will often go to the shrine for blessings before leaving for school or work. At other times one may sit alone in the shrine, pray and chant the names of God, read from scripture, meditate silently or sing devotional songs.
Temple Worship
Hindus prefer to live within a day’s journey of a temple. The temple is a special building, revered as the home of God. The main Deity is enshrined in the temple’s central sanctum. In India, there are hundreds of thousands of temples, most quite ancient. Temples in India can be enormous, covering many acres, having vast pillared hallways that can accommodate 500,000 devotees during a festival. Often one or more families of priests oversee the temple and conduct the worship over many generations. When Hindus migrate outside India, they build a temple as soon as possible. At first, community leaders themselves conduct the daily rituals. Later, professional priests are hired. There are now hundreds of Hindu temples in America. The largest are in New York, Pennsylvania, Illinois, Texas and California.
The temple worship ceremony, or puja, is usually performed by a priest from India. During the ceremony, he worships God by chanting Sanskrit verses from the scriptures and performing arati. Arati is the waving of an oil lamp in front of the Deity while bells are rung. The priest also offers flowers, sweets and fruit. These offerings are then distributed to the devotees as a blessing from God. Hindus may visit the temple throughout the day to worship and meditate.
Hinduism’s Saints, Teachers and Swamis
Hinduism has a rich history of saints and sages, both men and women. Their lives are educational and inspiring. They come from all castes. Some saints, such as Adi Shankara, have written detailed explanations of the Vedas and other scriptures. Other saints, such as Mirabai, Tukaram and Sambandar, taught through devotional songs. Recent saints include Sri Ramakrishna and Anandamayi Ma. Their deeply religious lives have uplifted millions of Hindus and others worldwide.
There are hundreds of thousands of religious scholars and teachers, both men and women, known as pundits. Some give spellbinding discourses on sacred scriptures, including Ramayana and Mahabharata. Tens of thousands may attend such gatherings, which include storytelling, preaching, devotional singing and drama. These events often go on for days or even a month.
Hinduism has millions of swamis and other holy persons. Swamis are unmarried men (and some women) who have taken up spiritual life full time. Swami means “he who knows himself.” Some live in monasteries; others wander as homeless mendicants. Swamis are the religious ministers of Hinduism. Many swamis teach, others run large institutions that perform social service for their communities, and still others live alone and meditate long hours each day in their pursuit of divine enlightenment. Special among these are the holy gurus. Gu means darkness and ru means remover. So guru literally means “the one who removes darkness.” These men and women are great religious teachers, some with millions of followers. Several gurus have popularized the Hindu practice of yoga by establishing training centers all over the world. No one person or institution is in charge of Hinduism. Instead, there are thousands of independent spiritual traditions, monastic orders and religious institutions.
The Yearly Festival Cycle
There are many religious festivals celebrated by Hindus each year. They are observed at home, in temples and public places. Most Hindu festivals are observed according to an ancient solar-lunar calendar. Several festivals honor the avatars of Lord Vishnu. For example, Ram Navami celebrates the birth of Lord Rama in March/April. Krishna Janmashtami, in July/August, celebrates the birth of Lord Krishna.
Mahasivaratri takes place in February/March, when devotees fast and worship the transcendent Lord Siva all night in the temple. Diwali, or Dipavali, is the biggest festival of the year. It is dedicated to Lakshmi, the Goddess of Wealth, and takes place in October/November. Navaratri is the second largest festival. It lasts nine days and takes place in September/October. It is dedicated to the worship of the Goddess, Shakti. in her three forms: Durga, the Goddess of Protection; Lakshmi, the Goddess of Wealth, and Sarasvati, the Goddess of Knowledge.
Holi, in March/April, is a highly spirited festival where everyone sprinkles each other with colored water and powders. It signifies the triumph of good over evil and marks the beginning of the winter crop harvest. Vaikasi Visakham (May/June) is sacred to Hindus, Buddhists and Sikhs. Guru Purnima is a special festival to honor one’s spiritual teacher, or guru. It takes place on the full moon day in July. There are also many social festivals in India, such as Pongal. It is held in January and celebrates the incoming harvest.
One special festival, the Kum-bha Mela, takes place in a twelve-year cycle. Hindu saints and millions of devotees travel to certain sacred rivers at an auspicious time for worship. The 2001 Kumbha Mela was held at Prayag (modern Allahabad) in North India. It was attended by 70 million people, including 30 million on January 24 alone. This was the largest religious gathering ever held on the Earth.
Summary
Hinduism is the oldest world religion. It accepts that there are many ways to worship God. It has endured for so long because the religion and culture have instilled in each Hindu a unique and strong sense of identity and community. The Rig Veda concludes, “Let there be everlasting unity and peace among all human beings.”
Key Terms:
samskara, bindi, puja, swami, Kumbha Mela
Hinduism Today’s Teaching Standards
8. Describe the spread of Hinduism outside of India in ancient and modern times.
9. Describe the daily observances of Hindus, home and temple worship, religious teachers and the major festivals.
10. Explain how Hinduism has survived over the last 5,000 years.
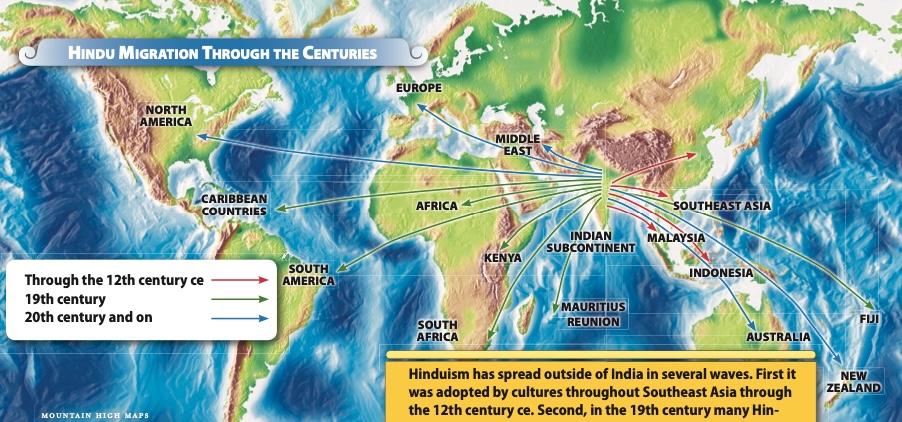
Hinduism has spread outside of India in several waves. First it was adopted by cultures throughout Southeast Asia through the 12th century ce. Second, in the 19th century many Hindus moved to the various European colonies, such as South Africa, the Caribbean and Fiji. And most recently, Hindus migrated to more than 150 countries in the 20th century. There are Hindu temples in nearly every country of the world
Academic Vocabulary
indentured – under contract to work for a certain number of years
austerity – a difficult practice of self-denial and discipline
meditate – think deeply about, go within yourself or seek God within
mendicant – a holy person who lives by begging
auspicious – a favorable time–for the Mela, as determined by the Hindu calendar
The bell is used in Hindu worship because it can be heard in the world of the Gods
The sacred oil lamp is used in the home and temple. Many Hindu events begin with the lighting of the lamp.
Linking to Today
Festivals
The biggest Hindu festival of the year is Diwali, or Dipavali, the Festival of Lights, celebrating the victory of good over evil, light over darkness. It takes place for five days around the new moon in October/November. It also honors the return of Lord Rama to Ayodhya after 14 years in exile. Lakshmi, the Goddess of Wealth is invoked for prosperity, and Her presence is felt in every home. Hindus thoroughly clean the house, take a special bath and put on new clothes. Thousands of small lamps, including traditional clay oil lamps (pictured at right), are placed everywhere and fireworks signal hope for mankind. It is a national holiday in India and in many countries with large Hindu populations. Some Hindu festivals take place mostly at home, such as Raksha Bandhan, which is on the full moon in July/August. Sisters tie a rakhi, or colored thread, around the wrist of their brothers. In return, the brother gives his sister a present and promises to protect her. The rakhi can also be given to anyone chosen as an “adopted brother.”
Section 3 Assessment
Reviewing Ideas, Terms and People
1. a. List What are the five basic practices of Hinduism?
b. Define What does the bindi, red dot, signify?
c. Explain How do Hindus use their home shrine room?
2. List What are the various kinds of priests and holy men and women in Hinduism?
3. a. Explain What is the year’s biggest Hindu festival?
b. Define What is the meaning of the rakhi bracelet?
c. Recall What is special about the Kumbha Mela?
d. Elaborate Why has Hinduism lasted so long?
4. List Make a list of three columns. In the first column write the name of a major Hindu festival. In the second, put the time of year it occurs. In the third list what it celebrates.
Focus on Writing
5. Understanding Hindu practices
Why do you think Hindus want to live near a temple?
Internet Resources:
Go to http:/www.hinduismtoday.com/education/ [http:/www.hinduismtoday.com/education/ ]for a PDF version of this lesson with clickable links to resources. Also at the same url are additional teaching resources and letters of endorsement from academics and community leaders. To order additional copies of this educational insight, go to http:/www.minimela.com/booklets [http:/www.minimela.com/booklets/]